“`html
Top 5 Proven Steps to Become a Dermatologist in 2025
Becoming a dermatologist is a rewarding career path that merges medical science with patient care focused on skin health. As dermatologists, these specialists tackle a variety of skin diseases, perform dermatology procedures, and offer cosmetic solutions to patients. If you are exploring how to become a dermatologist, this article will guide you through the essential steps for shaping your career in dermatology by 2025.
Understanding the Dermatologist Career Path
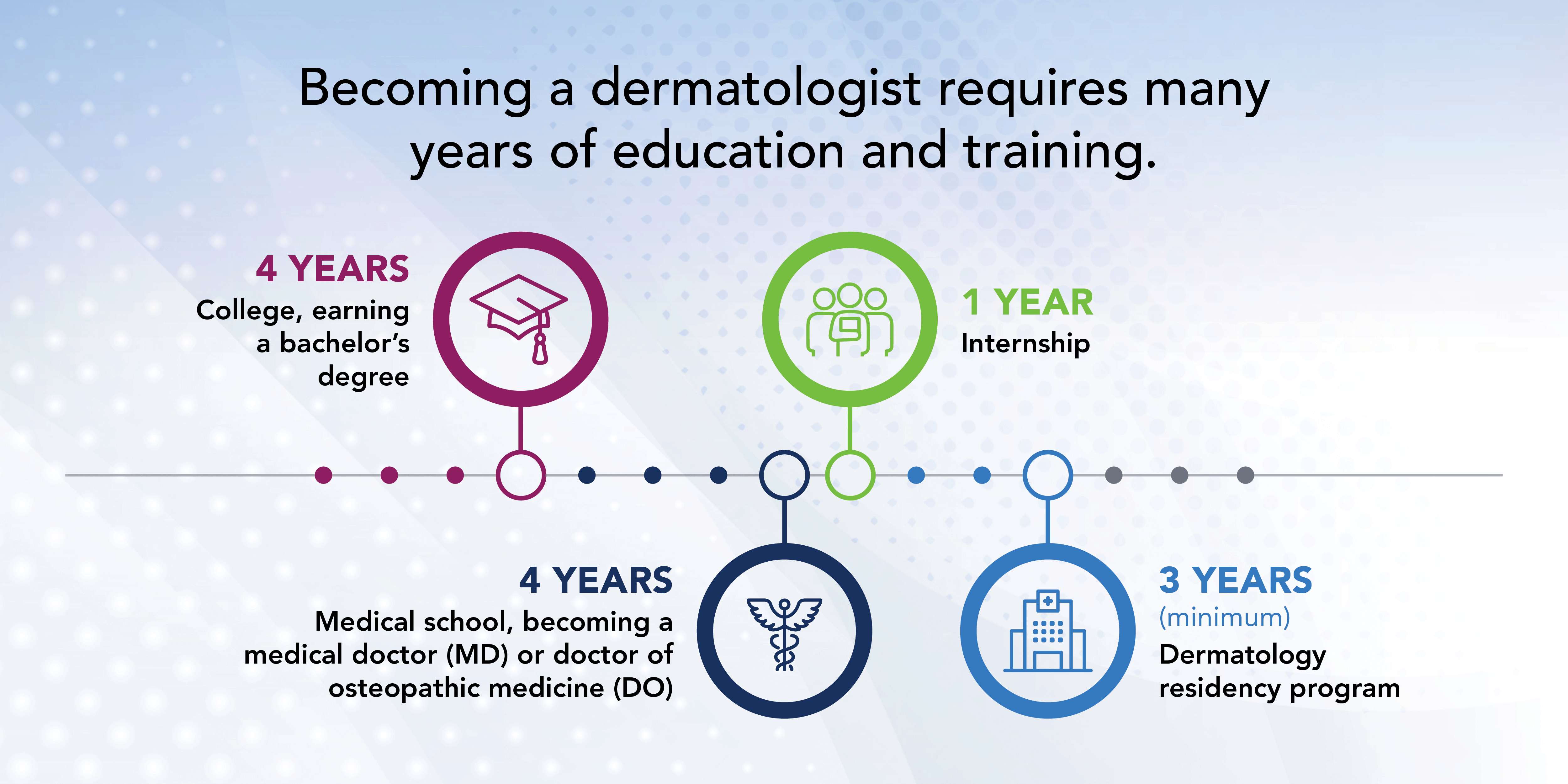
The journey to a successful career in dermatology begins with a clear understanding of the dermatologist career path. It typically requires extensive education and training. This path involves earning a bachelor’s degree, attending medical school, completing residency training, and obtaining board certification. At each step, aspiring dermatologists gain critical knowledge about skin conditions, dermatology exams, and various treatment options like acne treatment, skin cancer treatment, and eczema management. Familiarizing yourself with this career trajectory ensures you can meet the necessary medical school requirements and select suitable internships.
Step 1: Earn a Bachelor’s Degree
Before diving into medical school, you need to earn a bachelor’s degree in a science-related field, such as biology or chemistry. This stage is crucial as it lays the groundwork for your understanding of human anatomy and physiology. Engaging in summer shadowing programs with practicing dermatologists provides valuable insight into day-to-day operations, including patient consultations and the importance of patient care in dermatology. Utilize this time to volunteer in health centers to build a strong background in patient interactions.
Step 2: Complete Medical School
Upon obtaining your degree, the next step is enrollment in medical school, where you will delve into the complexities of human health and integrative medicine. The curriculum will cover foundational concepts in skin diseases, the physiology of the skin, and applicable treatment modalities. During your clinical rotations, focus on the dermatology specialty to gain hands-on experience with skin assessments and dermatological imaging techniques.
Step 3: Pursue Residency Training
After medical school graduation, you will enter a residency program, where you will specialize in dermatology. This stage typically lasts three years and emphasizes critical training in various aspects of dermatology, including clinical dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, and dermatopathology. Engaging with multidisciplinary dermatology teams enhances your learning experience and prepares you for real-world scenarios in managing diverse patient cases.
Board Certification and Beyond
Reaching the stage of board certification solidifies your dermatologist qualifications as a trusted medical professional. Becoming board-certified is pivotal as it distinguishes you in a competitive field and assures patients of your expertise.
Step 4: Achieve Board Certification
To become board certified, you must pass rigorous examinations conducted by the American Board of Dermatology. The exams assess your competence in diagnosing and treating various skin conditions, procedural skills, and patient management practices. Once certified, you can practice independently, but remember that continuing education for dermatologists is crucial. Regularly attending dermatology conferences keeps you updated on emerging dermatology technologies and advanced techniques, such as laser treatments.
Step 5: Consider Fellowships and Subspecialties
While board certification allows you to begin your practice, many dermatologists opt for additional training and dermatology fellowships. Fellowships, which typically last one year, offer opportunities to specialize further in areas like skin cancer treatment, cosmetic dermatology, or pediatric dermatology. This added expertise can enhance your resume and increase your chances of securing desirable positions post-training.
Patient Care and Future Prospects in Dermatology
A dedicated dermatologist must prioritize patient care and tailor treatment plans based on individual needs. With a growing dermatologist job outlook, it’s crucial to adapt to evolving medical practices and technologies.
Integrating Telemedicine in Dermatology
Telemedicine is reshaping patient interactions and expanding access to dermatological care, particularly for patients in rural areas. Implementing telehealth services enables dermatologists to offer consultations remotely, monitor treatment progress, and maintain patient engagement. Understanding effective strategies for dermatology patient consultations via telehealth will be invaluable as you guide your future practice. By engaging with patients through this medium, you can instantly assess skincare products and treatment efficacy.
Ensuring Community Education and Outreach
As a practicing dermatologist, community service in dermatology is crucial. Educating the public about common skin conditions and creating awareness through programs can significantly impact public health. Participate in outreach programs to disseminate information on harmful sun exposure and highlight essential skin care practices. Engaging in dermatological innovations and developing healthcare initiatives can empower individuals to focus on their skin health long before they require treatment.
Key Takeaways
- The journey to becoming a dermatologist requires a thorough understanding of medical education and extensive training.
- Pursuing fellowships and specialized training areas further enhances your qualifications.
- Emphasize continuing education to remain abreast of the latest advancements in dermatology.
- Leveraging telehealth services and community outreach can lead to impactful patient care.
- Preparing for a career in dermatology is not just about education; it involves a passion for skin health and patient advocacy.
FAQ
1. What are the main medical school requirements to become a dermatologist?
The medical school requirements typically include completing a bachelor’s degree with a pre-med focus, passing the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT), and applying to accredited medical schools. Additionally, gaining clinical experience through internships is highly recommended.
2. What are the different dermatology specialties?
Dermatologists can specialize in various fields, including cosmetic dermatology, dermato-oncology (skin cancer treatment), pediatric dermatology, and dermatopathology. Each offers unique opportunities to address specific skin concerns.
3. How important is board certification for dermatologists?
Board certification is crucial as it establishes your competence and expertise in the field of dermatology. It enhances your credibility and can impact job prospects within dermatology clinics and healthcare systems.
4. What role does continuing education play in a dermatologist’s career?
Continuing education for dermatologists is essential for staying updated on emerging dermatology technologies and treatment methodologies. Participation in workshops and conferences promotes professional growth and improves patient care.
5. Can telemedicine be effectively used in dermatology?
Yes, telemedicine is effectively utilized in dermatology for patient consultations, follow-ups, and monitoring treatment adherence. It expands access to care by connecting dermatologists with patients who may have difficulty visiting a clinic in person.

“`