How to Properly Calculate Percent Yield for Successful Experiments in 2025
Understanding how to **calculate percent yield** is crucial for anyone conducting experiments in a laboratory setting. Percent yield, a key concept in **chemistry**, provides insight into the efficiency of a chemical reaction and helps evaluate the performance of an experiment. This article will explore the **percent yield formula**, practical examples, and methods to improve yields. We’ll also look at factors affecting yield and how to accurately measure yield for successful experiments.
The Importance of Percent Yield in Chemistry
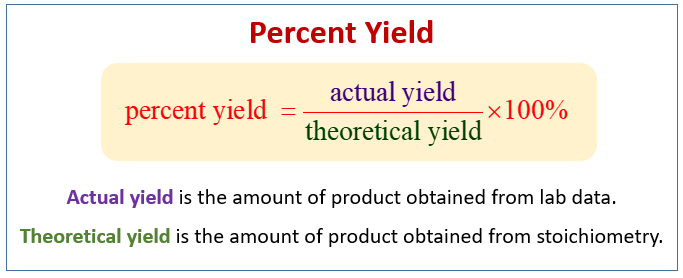
The significance of **percent yield in chemistry** cannot be overstated. Percent yield indicates the efficiency of a chemical reaction by comparing the **actual yield** obtained with the theoretical yield expected from stoichiometric calculations. Understanding the **yield percentages in experiments** allows chemists to optimize their methods and materials, ultimately leading to better results. For example, in an experiment aimed at synthesizing a compound, a low percent yield can signify inefficiencies or errors in the reaction process.
Theoretical vs. Actual Yield
The first step to calculating percent yield is understanding the distinction between **theoretical yield** and **actual yield**. Theoretical yield is the maximum amount of product expected based on balanced equations and stoichiometric calculations. In contrast, actual yield is the amount of product actually produced in an experiment. To find the percent yield, use the formula:
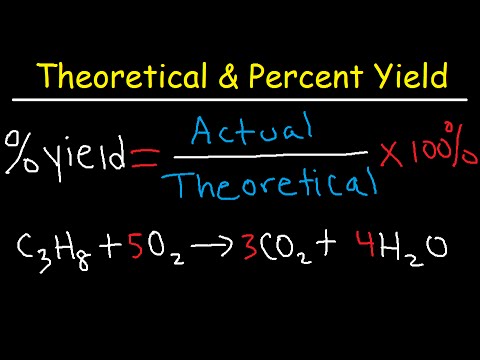
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100. For instance, if a reaction is supposed to yield 100 grams of product but only 80 grams are produced, the percent yield is 80%.
Yield Calculation Methodology
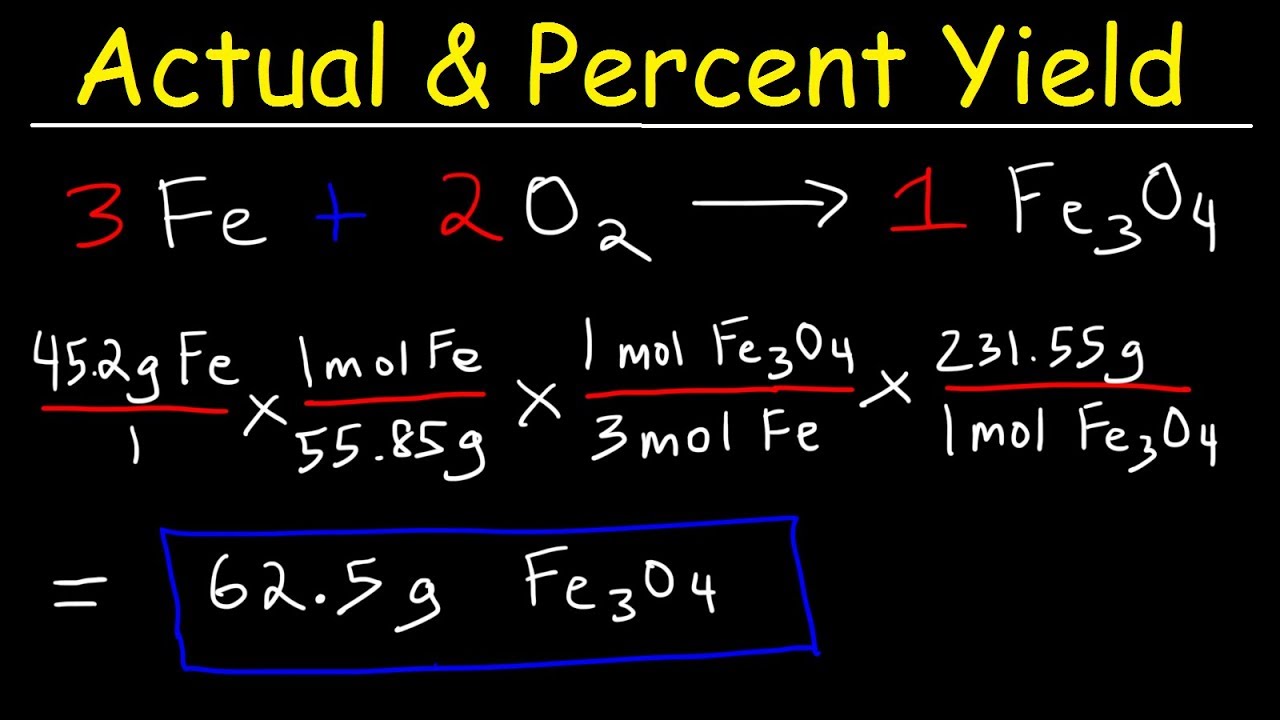
To perform accurate **yield calculation in chemistry**, the following steps can be followed: 1) **Calculate the theoretical yield** of your product using stoichiometry based on the balanced equation. 2) **Conduct your experiment** and measure the actual yield of the product formed. 3) **Substitute your values** into the percent yield formula. This straightforward method ties into the broader context of **yield metrics**, allowing you to analyze and understand the outcomes of your experiments effectively.
Factors Affecting Percent Yield
Several factors can influence the **percent yield** of a chemical reaction. A deep understanding of these factors can improve the accuracy of your yield assessments and experiments. Key factors include reaction conditions, the purity of reactants, and measurement accuracy. Each plays a pivotal role in determining the **yield in chemical reactions** and understanding how to harness these factors can lead to improved performance in future experiments.
Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions, such as temperature and pressure, significantly impact the **efficiency of yield**. Many reactions are sensitive to these conditions; varying them might enhance or reduce product formation. For instance, increasing temperature can accelerate reaction rates, often resulting in a better yield if managed correctly. On the other hand, a high temperature can lead to unwanted side reactions, ultimately lowering the yield.
Purity of Reactants
The purity of reactants is another critical factor affecting **percent yield**. Impurities can lead to unexpected by-products or lower amounts of the desired product. For example, if you start with reactants that are only 90% pure, the overall percent yield calculation could be flawed because you’re not starting with the ideal stoichiometric amounts. Ensuring that your reactants are as pure as possible will provide a more accurate reflection of the yield achieved.
Improving Percent Yield in Experiments
Enhancing **percent yield** is a common goal for chemists, as higher yields can lead to more efficient and cost-effective experiments. Various techniques exist to improve yields, and understanding these options allows chemists to apply them appropriately in their own research.
Yield-Enhancing Techniques
Some effective **yield-improving strategies** include optimizing reagent concentrations, adjusting temperature and pressure, and ensuring thorough mixing. For example, increasing the concentration of reactants can sometimes push the reaction to completion, resulting in higher actual yields. It’s essential to adjust these parameters methodically and iteratively to find the optimal conditions that maximize your **yield efficiency**.
Accurate Measurement Practices
Implementing **accurate yield measurement techniques** is vital for determining the true efficacy of your experiments. Always use calibrated scales for measuring actual yield and apply consistent procedures for collecting data. Regular training in measurement techniques and being open to using digital tools for data collection can also cater to significant improvements in accurately assessing yields. Also, logging all experimental conditions and outcomes can assist in reflective evaluations for future experiments, aiding in **yield calculations with examples** over time.
Practical Example of Percent Yield Calculation
To solidify your understanding, let’s look at a practical example. Suppose you conduct an experiment aiming to synthesize 50 grams of a biphenyl from phenylboronic acid and aryl halide through a cross-coupling reaction. After completing the process, you recover 37 grams of biphenyl. Here’s how to calculate the percent yield:
- Theoretical yield (from calculations) = 50 grams
- Actual yield (measured) = 37 grams
- Percent yield calculation: (37 g / 50 g) x 100 = 74%
This calculated yield percentage demonstrates the efficiency of your experiment and aids in assessing the overall effectiveness of your synthesis methodology.
Key Takeaways
- Percent yield is a crucial metric in evaluating the efficiency of chemical reactions.
- Understanding both theoretical and actual yield is essential for calculating percent yield accurately.
- Several factors, including reaction conditions and the purity of reactants, significantly influence percent yield.
- Various strategies exist for improving yield, including careful measurement practices and appropriate adjustments to reaction conditions.
- A practical understanding of yield calculation can optimize experimental outcomes in chemistry.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of calculating percent yield in chemistry?
Calculating percent yield is significant because it allows chemists to evaluate the efficiency of their experiments. A high percent yield indicates that a reaction proceeds well, while a low percent yield may signal the need for method improvements or error identification in the experiment.
2. How can I improve percent yield in my experiments?
Improving percent yield can be achieved by optimizing reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and reactant concentrations. Furthermore, ensuring the purity of reagents and accurate measurements also plays a crucial role in enhancing yields.
3. What are some common methods to calculate percent yield?
The most common method to calculate **percent yield** is to use the formula: Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100. By substituting the obtained actual yield and the theoretically calculated yield into this formula, you can determine the efficiency of your reaction.
4. What factors can lead to yield loss in a chemical reaction?
Yield loss can occur due to various factors, including side reactions, incomplete reactions, and losses during product recovery. Understanding these factors allows chemists to refine experimental procedures to minimize yield loss and enhance results in their experiments.
5. Can high percent yields indicate a problem?
Yes, an unusually high percent yield might indicate errors such as during measuring techniques, contamination, or unintended reactions. Thus, it’s essential to analyze all factors contributing to the results to ensure the validity of yield percentages in your experiments.
6. How does stoichiometry play a role in yield calculations?
Stoichiometry is integral to determining theoretical yield, which serves as the baseline for all yield calculations. By accurately balancing chemical equations and understanding the ratios of reactants and products, chemists can predict expected yields more effectively, helping them achieve better actual yields in practice.
For more detailed insights and examples, visit our articles on calculating yield and improving percent yield practices.