Understanding Marginal Cost: Definition, Calculation, and Importance in 2025
What is Marginal Cost?
Marginal cost refers to the additional expense incurred when producing one more unit of a good or service. Understanding the **marginal cost definition** is crucial for businesses because it directly affects pricing strategies, production efficiency, and overall profitability. Essentially, marginal cost plays a pivotal role in determining the optimal level of production. It helps firms assess if the cost of producing an additional unit is justified by the revenue it generates. This concept is pivotal in economics and finance, especially when analyzing **marginal cost in business** decisions.
Key Components of Marginal Cost
The **marginal cost formula** can be expressed simply as: MC = ΔTC/ΔQ, where ΔTC is the change in total cost and ΔQ is the change in output quantity. This formula underscores two main aspects: fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs, such as rent, do not change with the production level, while variable costs vary proportionally with output. Understanding how these components interact underlines the significance of **fixed costs and marginal cost** in making informed production and pricing decisions.
How Marginal Cost Influences Decision-Making in Economics
Analyzing **marginal cost versus marginal revenue** is essential for determining the most profitable level of production. A key takeaway is that as long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, the firm can increase profit by producing more. When businesses work within this framework, they can better align their **production decision-making** strategies with market demands, leading to improved financial outcomes. Thus, understanding these economic principles can guide firms toward achieving greater efficiency.
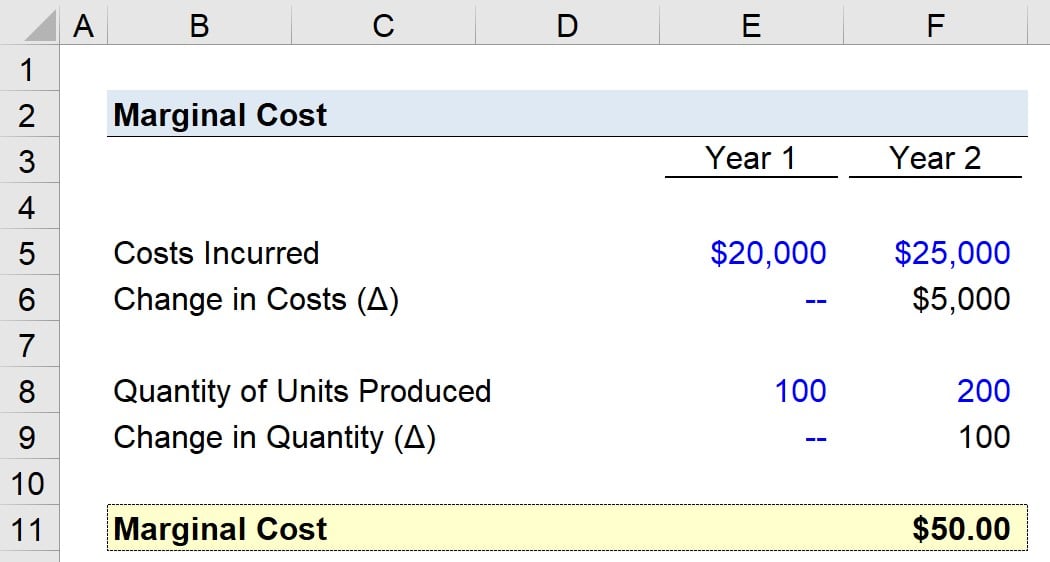
How to Calculate Marginal Cost
Calculating marginal cost involves using data from the company’s **total cost analysis**. To compute the marginal cost accurately, you will need to observe changes in production levels and the corresponding changes in costs. It is a step-by-step process that requires precise data on fixed and variable costs associated with production layers.
Step-by-Step Guide to Marginal Cost Calculation
Here’s a practical example of **how to calculate marginal cost**: Assume a company produces 100 units of a product at a total cost of $500. If producing 101 units increases the total cost to $505, the marginal cost for the additional unit is calculated as follows: MC = ($505 – $500)/(101 – 100) = $5. This simple example illustrates the fundamental method for determining the marginal cost. By maintaining meticulous records of production levels and associated costs, a business can routinely compute and evaluate its **marginal cost** efficiently.
Marginal Cost Alongside Average Cost
Understanding the relationship between **marginal cost and average cost** is equally important. While marginal cost focuses on the expense of producing one additional unit, average cost considers the total cost per unit across all units produced. Businesses often analyze both metrics to gauge overall efficiency and profitability. Generally, when marginal cost is less than average cost, producing more units can reduce average costs, thereby promoting **cost minimization** strategies.
The Importance of Marginal Cost in Business Strategy
Understanding the importance of marginal cost is vital for making strategic business decisions. It can aid companies in creating pricing models that align with market demand and internal cost structures. Insights gained from analyzing marginal cost help businesses evaluate their **cost management strategies**, ensuring that they can adjust to economic conditions and remain competitive in their industries.
Developing Optimal Pricing Strategies
Implementing effective **marginal cost pricing** is a technique where businesses set prices that reflect the cost incurred to produce an additional unit. This ensures that the firm covers its costs while remaining competitive within the market. Additionally, knowing the **impact of production on cost** is essential for businesses aiming to price their products strategically, ensuring profitability without alienating customers through high prices.
Linking Marginal Cost with Profit Margins
Integrating marginal cost analysis with **profit margin analysis** can reveal insights regarding product pricing and cost efficiency. For example, a firm must earn more per unit than its marginal cost to achieve profitability. This relationship underscores the significance of financial management decisions based on solid understanding of **marginal cost in production**. It enables firms to tackle various pricing scenarios, testing how price elasticity will affect **consumer surplus** and overall market demand.
Visualizing Marginal Cost through Graphs
A **marginal cost graph** visualizes the relationship between the number of units produced and the corresponding marginal cost, which typically decreases initially due to economies of scale but can increase as production reaches capacity limits. This graph is crucial for understanding efficiency in production capabilities and adjusting strategies accordingly.
Understanding the Marginal Cost Curve
The **marginal cost curve** is a graphical representation of the cost to produce each additional unit. Initially, the curve might decline due to efficiencies gained with increased production, but it will eventually rise as resources become strained. By studying this curve, businesses can identify the optimal production level where marginal costs equal marginal revenues, allowing them to maximize profits. Documenting production data over time aids in forecasting future impacts on **operational efficiency** and helps guide resource allocation decisions.
Connecting Marginal Costs to Economic Environment
External factors including market competition, supply chain dynamics, and economic conditions can influence **marginal cost predictions**. Businesses must stay informed about these factors to adapt their strategies continually. Understanding these effects allows companies to stabilize production costs, making **economic analysis** a critical aspect of forward planning in today’s business climate.
Key Takeaways
- Marginal cost is crucial for determining pricing and production decisions.
- Understanding the components of marginal cost helps optimize financial strategies.
- Calculating marginal cost requires a clear analysis of changes in total costs corresponding to output levels.
- Visual tools such as marginal cost graphs aid in strategic decision-making.
- Continuous monitoring of financial implications leads to successful resource allocation.
FAQ
1. What are fixed costs and how do they relate to marginal cost?
Fixed costs are expenses that do not change with the level of goods or services produced. They are crucial in the context of tasting financial situations relating to **marginal cost** because they are integrated into total production costs but don’t fluctuate with changes in output. Understanding how fixed costs impact total costs can significantly affect pricing strategies and overall financial management.
2. Why is marginal cost important for pricing strategies?
**Marginal cost** provides essential insights for setting prices based on production costs. Businesses must ensure that the price of their goods covers the marginal cost to remain profitable while remaining competitive in the market. Without understanding marginal costs, firms risk underpricing their products or incurring losses on additional production.
3. How do variable costs affect marginal cost calculations?
Variable costs fluctuate with the scale of production, making them integral to **marginal cost calculations**. When calculating **marginal cost**, understanding how variable costs affect total costs at different output levels is crucial. As production increases, knowing the variable cost per unit is imperative to accurately assess if producing additional units will yield a profit.
4. What implications does marginal cost have on profitability?
The relationship between marginal cost and revenue is pivotal in assessing profitability. If the marginal cost exceeds the marginal revenue, the company may face losses on increasing production. Therefore, maintaining a balance where revenue consistently exceeds marginal costs is crucial to maintaining healthy profit margins.
5. How can I implement marginal cost analysis in my business?
To implement **marginal cost analysis**, start by gathering accurate data regarding total costs and production levels. Utilize the marginal cost formula to calculate costs for additional units. Integrate these findings into pricing strategies and production decision-making processes to optimize resource allocation and maximize profitability. Regularly review and adjust strategies based on market changes and internal cost analysis.