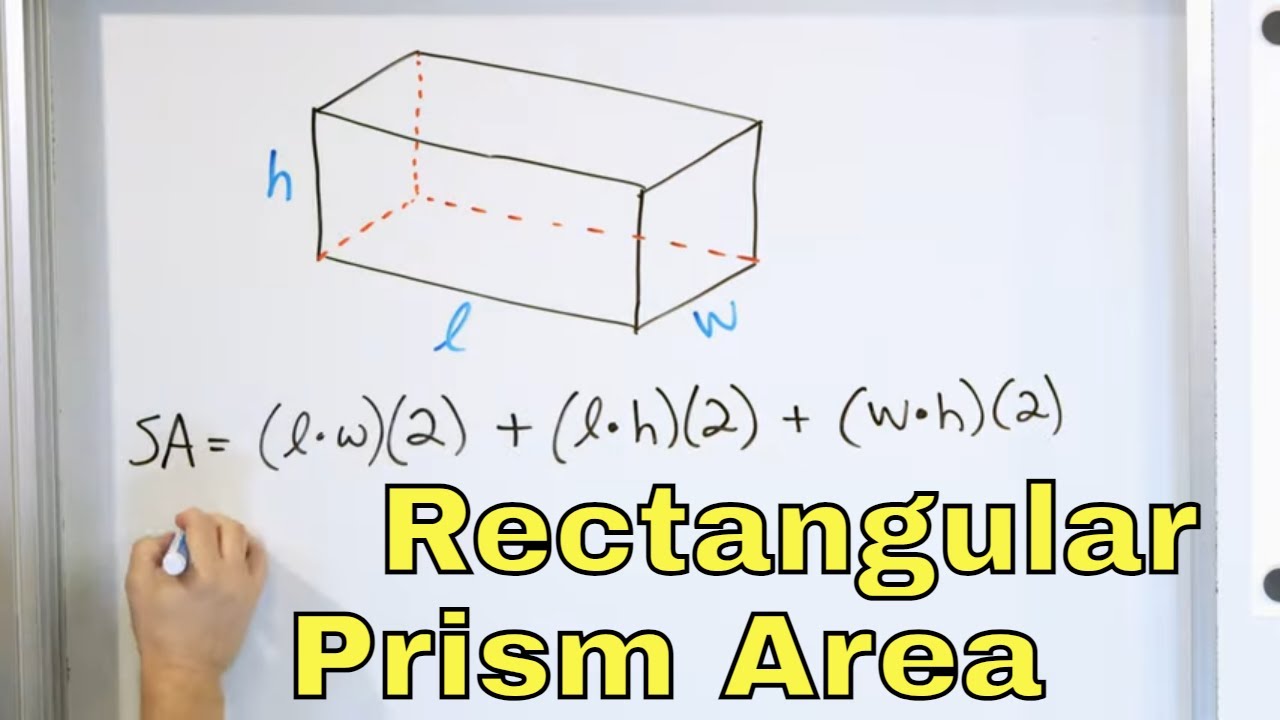
Effective Ways to Calculate the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
Understanding the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
The **surface area of a rectangular prism** represents the total area of all its external faces. It is a fundamental concept in geometry, particularly in the study of **3D shapes**. When calculating the **total surface area**, we consider the prism’s dimensions, namely its **length, width, and height**. The surface area can be particularly important in various fields such as architecture and construction, where understanding the **rectangular shape properties** can help in material estimation. To derive the formula effectively, one must be adept at **calculating dimensions** accurately and understanding mathematical operations on surfaces.
The Formula for Surface Area
The formula for calculating the **surface area** of a rectangular prism is given by:
Surface Area = 2(lb + bh + hl)
In this equation, \( l \) stands for length, \( b \) for breadth (or width), and \( h \) for height. To derive this formula, one can visualize the prism as having six faces made of rectangles. By **adding areas** of each rectangular face—two for each distinct pair of dimensions—we achieve the total area. For example, if a rectangular prism has dimensions of 2m in length, 3m in width, and 4m in height, substituting these values into the formula yields a total surface area of 2(2*3 + 3*4 + 4*2) = 2(6 + 12 + 8) = 2*26 = 52 m².
Practical Applications of Surface Area Calculation
Knowing how to calculate the **surface area of a rectangular prism** possesses various real-world applications. In construction and architecture, these calculations guide the **area measurement techniques** necessary for determining the quantity of paint required for walls, the fabric needed for reupholstering furniture, or the coatings needed for insulation. For example, a building contractor would use surface area concepts when considering materials that require surface coverage, ensuring that cost estimations are as accurate as possible when determining the necessary materials.
Calculating Dimensions Using Surface Area
Often, difficulty arises when needing to find one or more dimensions of a prism given the **total surface area**. Understanding relationships between area dimensions and proper manipulations can lead to effective solutions. When given the surface area, one can rearrange the formula accordingly to solve for one of the dimensions if the others are known. This mathematical flexibility emphasizes the importance of **understanding prisms** in geometry.
Step-By-Step Calculation Example
To demonstrate how to use the surface area formula for **finding volume and surface area**, consider the following practical example. Suppose a rectangular prism has a total surface area of 54 m², with its height measured at 3m and its length at 5m. To find the width, we start with the surface area formula:
54 = 2(5*3 + 3*w + 5*w)
By simplifying this equation, we find:
54 = 2(15 + 8w)
27 = 15 + 8w
Solving for \( w \) gives:
8w = 27 – 15
8w = 12
w = 12/8 = 1.5 m
This example highlights the process of utilizing the **surface area equation** to derive dimensions, connecting the dots of geometric principles with real applications.
Common Challenges in Surface Area Calculations
<pWhile formulas greatly facilitate surface area calculations, several common challenges disrupt the flow of mathematical endeavors. Misunderstanding of measurement units or conversion errors can lead to inaccurate results. It's crucial to maintain consistency in using units, especially in applications requiring precision in **area measurement**. For instance, in a science experiment calculating fluid containment capacity, accurate surface area calculations could affect outcome reliability. Furthermore, many learners find **calculating surface areas of shapes** challenging due to improper grasping of geometric properties.
Visual Representations of Rectangular Prisms
Utilizing visual aids greatly assists in understanding the properties of **rectangular prisms**. Diagrams depicting various prisms highlight their faces, facilitating intuitive comprehension of their structure and functional areas. Resources such as charts outlining **rectangular prism dimensions** and physical models used in classrooms enhance learning experiences. Effective visualization strengthens connections between abstract concepts and practical measurement applications in both everyday life and prospective careers in STEM.
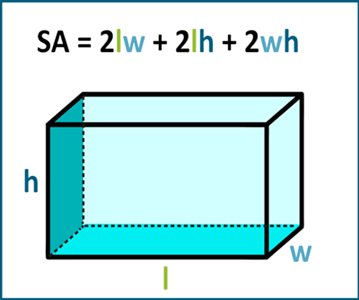
The above image provides a visual guide to help students grasp the **total surface area formula** more intuitively.
Using Rectangular Prism Nets for Surface Area Calculations
The concept of **rectangular prism nets** is helpful in visualizing how the prism’s surface area is composed of its individual faces laid flat. When unfolded, these nets create a 2D shape that adds clarity to the **area of rectangles** used in calculations. Allowing students and professionals to see how rectilinear shapes can fit together aids in more effective comprehension and application of formulas in various dimensions. This becomes particularly vital in classrooms or situations encompassing teaching **geometry principles**, where such visualizations allow for hands-on engagement.
Importance of Visual Aids in Geometry
Visual aids are critical not just in grasping complex concepts, but also in stimulating efficient learning environments. In many educational settings, differing learning modalities exist; using diagrams, 3D models, and hands-on activities can cater to diverse student needs by ensuring data is accessible and engaging. Infusing these methods into geometry education, particularly in lessons involving **geometric calculations**, helps foster an appreciation for the connection between shapes and real-world applications.
Key Takeaways
- Calculated surface area is vital for practical applications in construction and design.
- Correctly utilizing formulas, such as the surface area formula, enables successful dimension finding.
- Visual representation aids can significantly improve comprehension of geometric shapes.
- Common challenges can be surmounted with careful attention to measurement units.
- Understanding geometric properties and their real-world utility fosters engagement with mathematical concepts akin to daily life experiences.
FAQ
1. What is the surface area formula for a rectangular prism?
The surface area formula for a rectangular prism is expressed as Surface Area = 2(lb + bh + hl). In this formula, \( l \), \( b \), and \( h \) represent the length, breadth, and height of the prism, respectively. This formula helps calculate the total area covering all external faces of the prism using basic area properties of rectangles.
2. How do you visualize the surface area of a rectangular prism?
Visualizing the surface area of a rectangular prism can be accomplished using geometric nets, which display all the faces of the prism laid flat. This gives a clear depiction of each rectangular face and helps in understanding the total surface area by showing how dimensions come together. Diagrams and interactive 3D models are also effective for demonstrating any geometric shape’s properties.
3. Can you find the dimensions of a rectangular prism if you know its surface area?
Yes, by rearranging the surface area formula, one can determine the unknown dimensions if the others are known. By substituting the known lengths and isolating the variable of interest, you can algebraically derive the desired measurement. This illustrates the interdependence among the prism’s dimensions and overall geometric relationships within mathematical calculations.
4. Why is calculating surface area important?
Calculating surface area has significant implications in various fields, such as construction, where material costing and waste reduction are vital. The ability to accurately assess the surface area informs decisions on the amount of covering or treatment needed for objects and structures. Knowing applications helps integrate geometry into practical daily scenarios, enhancing efficiencies and avoiding excess.
5. What role does surface area play in real-life applications?
Surface area is crucial in real-life contexts such as packaging, where the strength and quantity of materials are dependent on the total area exposed. Additionally, in environmental sciences, surface area affects heat loss, odor emissions, and volume calculations hence emphasizing its multi-faceted attributes within the domains of science, engineering, and design.