How to Format a Hard Drive for Enhanced Performance in 2025
Formatting a hard drive is an essential procedure to ensure optimal performance and management of your data storage needs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various approaches to formatting hard drives, whether internal or external, and provide clear steps and best practices to enhance drive performance. We will also touch on crucial aspects such as backing up data, selecting appropriate file systems, and troubleshooting common formatting issues.
Understanding Hard Drive Formatting Types
When it comes to **formatting hard drives**, it’s vital to understand the different **hard drive format types** available. Common types include **NTFS**, **FAT32**, and **exFAT**, each offering unique features suited for specific tasks. For instance, **NTFS** is preferred for larger files and allows for better security, making it a popular choice for internal drives in Windows environments. On the other hand, **FAT32** is widely used for compatibility with various devices but has a 4GB file size limit, which can be restrictive for larger video files or games.
Choosing the Best File System Format
When deciding **how to format hard drive options**, consider the usage of your device. For most **gaming systems** and modern computer applications, using **NTFS** provides the best performance. If your hard drive will mainly operate with older systems or devices like USB flash drives, opt for **FAT32**. For compatibility across Mac and Windows, **exFAT** may be the best compromise, allowing for larger files without the restrictions found in FAT32. Understanding these **file system formatting** choices can significantly influence your overall experience with storage management.
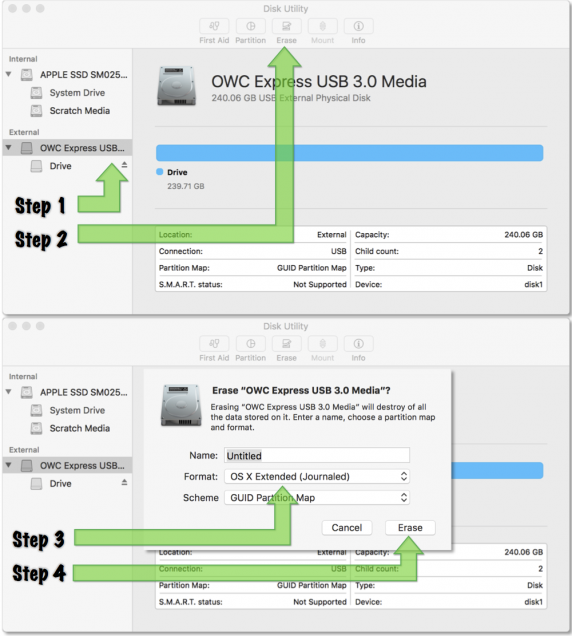
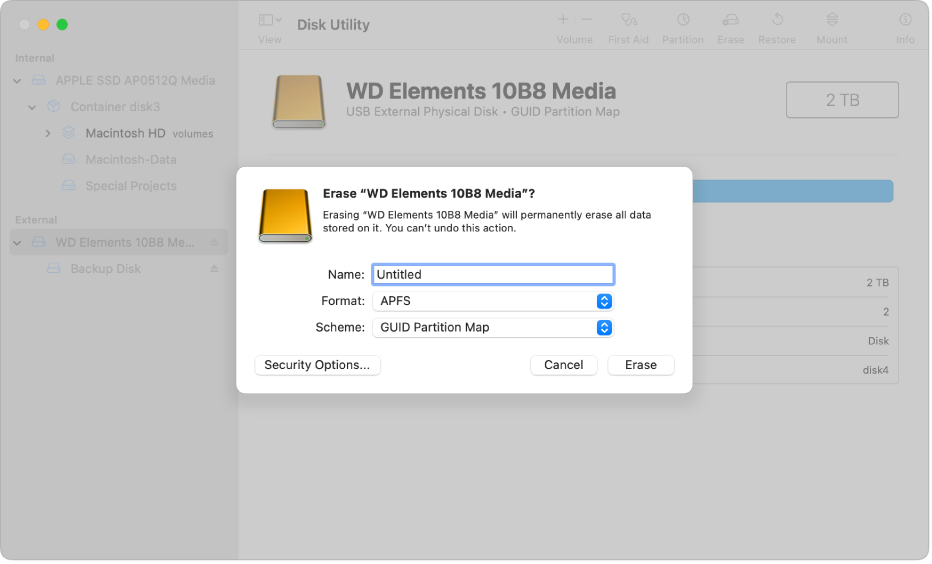
Steps to Format External Hard Drive
To quickly format an external hard drive: First, connect the drive to your system. On **Windows**, open the **Disk Management** tool, find the drive, right-click, and select “Format.” Ensure you select the right file system. For **Mac**, open **Disk Utility**, select the appropriate drive, and hit “Erase,” choosing the desired format. It’s crucial to **backup data before formatting** to avoid any permanent loss. Note that formatting different external drives may also vary based on their connection types, so always check compatibility beforehand.
The Internal Hard Drive Format Steps
Formatting an internal hard drive requires a careful approach, particularly if it contains the operating system. Begin by ensuring you have a secure backup of important data to reclaim storage space safely. Next, you will need a bootable USB or any **formatting tools for Windows**. After booting, you can partition or format the entire drive using the installation media. Following this procedure not only gives the system a fresh start but also can significantly boost performance.
Quick Format vs Full Format
Understanding the difference between a **quick format** and a **full format** is crucial in the formatting process. A **quick format** removes files from the disk but does not overwrite the disk’s surface, making data recovery possible using certain tools. In contrast, a **full format** deletes files and performs a sector-by-sector check, ensuring the integrity of the drive. For sensitive or used drives, opting for a **full format** is advisable, especially when planning to **erase data securely**.
Improving Hard Drive Performance
After formatting your hard drive, improving performance is often a key concern. Regularly executing **how to check hard drive health** procedures helps in identifying issues before they escalate. Tools available in **Windows** or **Linux** can optimize both SSDs and HDDs. Additionally, partitioning and formatting your drive can manage free space effectively, enhancing access time and resource allocation, especially when dealing with large files or running applications concurrently.
Preparing Hard Drives for Specific Uses
One size does not fit all when it comes to formatting hard drives for specific uses. **Formatting drives for video games**, for example, requires higher write speeds and optimized file structures to minimize lag. Configuring an SSD specifically for gaming can further enhance loading times and overall performance. For gaming purposes, a **quick format** using an NTFS file system is often ideal, plus using software to manage drive partitions can offer substantial improvements.
Using Disk Management for Format Options
The **Disk Management** utility is a powerful tool for users on Windows. Not only can you format a hard drive from this tool, but you can also manage partitions effectively. Just access it by right-clicking on **This PC** and selecting **Manage**, then navigating to **Disk Management**. Here, you can format, partition, or even expand disks as required. Moreover, you can also implement troubleshooting strategies if you run into **formatting hard drive issues**.
Best Practices for Formatting
Stick to the best practices for **safe formatting**. Before you make any changes, **backup data** thoroughly and verify the health of the hard drive. Employ quality formatting tools to minimize errors and ensure proper driver compatibility. Always guide the process by selecting logical partition sizes relevant to your usage needs. This way, you enhance overall efficiency in your storage system.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize different hard drive format types like NTFS and FAT32.
- Choose the file system according to your use case, emphasizing speed and device compatibility.
- Perform secure backups and pre-format checks to avoid data loss.
- Leverage disk management tools to simplify formatting and partitioning processes.
- Apply best practices for improved drive performance and reliability.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between NTFS and FAT32?
**NTFS** supports larger file sizes and offers enhanced security features—ideal for Windows systems that handle large amounts of data. **FAT32**, however, operates across more devices but has a file size limit of 4GB, making it less suitable for modern applications. Choose the file system that fits your specific requirements.
2. Can I recover data after formatting a hard drive?
Yes, data recovery is often possible after a format, especially with **quick formats**. However, the more securely data is wiped, the lower the chances of recovery. Using specialized recovery software can assist in undeleting files, but results are not guaranteed. Always ensure **backup strategies before formatting** are in place to mitigate data loss risks.
3. How can I securely erase my hard drive?
Secure erasure is done through tools that overwrite the drive’s existing data, ensuring it cannot be recovered. The **full format** method accomplished in **Disk Management** or through software can effectively accomplish this. For industries handling sensitive data, using a secure erase method specific to your drives is recommended.
4. What are common issues encountered during formatting?
Common problems include errors due to sector issues, wrong file system selections, or unreadable drives. Always ensure the drive’s health is checked before initiating the format process and try using different tools if you run into issues.
5. How do I check the health of my hard drive?
You can check hard drive health using built-in tools like **CHKDSK** in Windows or **Disk Utility** on Mac. Additional third-party applications can provide insights into the drive’s performance, longevity, and operational status, ensuring a better understanding of when to format.
In conclusion, formatting a hard drive involves understanding various formats, adhering to best practices, and taking calculated precautions to ensure data is managed effectively and securely.